Healthcare organizations may be sustained and the labor expenses associated with this services-driven business can be mitigated with the help of generative AI technologies. AI systems use sophisticated algorithms and enormous volumes of data to produce new insights, forecast results, and even develop remedies for difficult medical problems. For example, generative AI in clinical healthcare can help predict illness progression, personalize pharmaceutical regimens based on individual genetic profiles, and optimize treatment plans for patients with chronic disorders.
The ultimate goal is to improve the experience of patients and healthcare professionals, even if present implementations are primarily focused on cost-saving and automation in back-office processes.
Let’s examine practical instances of generative AI applications in the healthcare sector.
What Is Generative AI in the Healthcare Industry?
Drug development, customized treatment strategies, and more precise diagnosis are all made possible by generative AI. While merging with healthcare software development services is one of the operations in the healthcare industry that frequently need human intervention, generative AI can help with these processes.
Sorting through large amounts of data and logs by hand is a labor-intensive manual operation that is often involve in core administrative and corporate functions as well as interactions with patients and generative AI development companies. Regardless of the amount, generative AI can summarise this data and save important time.
These data-driven insights are changing hospital operations, improving care delivery generally, and transforming public health efforts. These changes will ultimately improve patient care and boost the sustainability of healthcare systems. From a macro perspective, GenAI is opening doors for a healthcare ecosystem that was previously unattainable due to its lack of responsiveness, patient-centeredness, and data enhancement.
Gen AI Use Cases in Healthcare
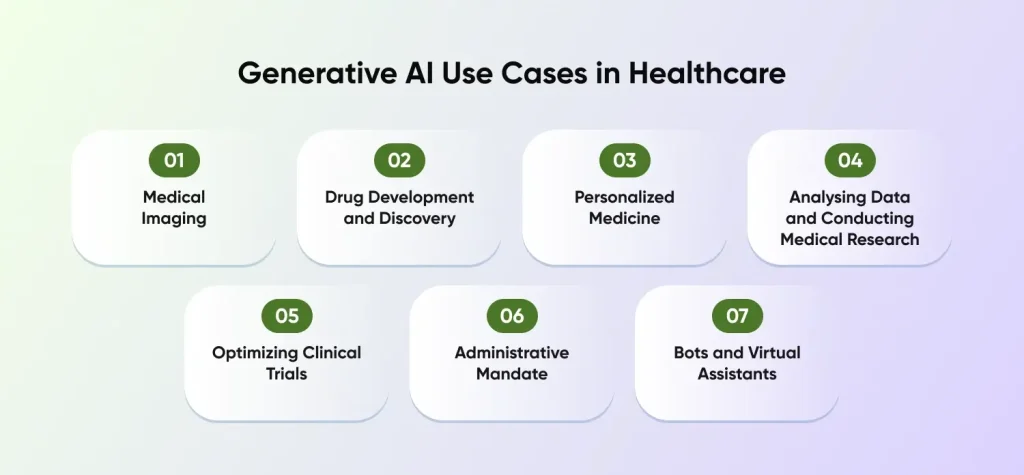
Generative AI has demonstrated considerable promise in several healthcare-related applications. Let’s study these use cases or examples in detail which gave rise to the healthcare technology trends of today.
1. Medical Imaging
Radiologists are using generative AI technology more and more to help them quickly and reliably diagnose diseases using X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans.
These algorithms, which were trained on a variety of patient data sets, find biomarkers that are suggestive of particular disorders, forecast the course of the disease, and recognize early indicators of a wide range of medical conditions, such as skin and lung malignancies, Alzheimer’s disease, and diabetic retinopathy. In addition to expediting the diagnostic process, generative AI increases accuracy, which results in earlier identification and better patient outcomes.
- Image Synthesis: Through the use of visually understandable representations, generative models create images of organs or tissues for educational objectives such as training medical practitioners and making medical conditions easier to explain to patients.
- Automated Segmentation: By using generative AI, medical picture analysis can be streamlined and time-saving for healthcare workers by automatically classifying organs or anomalies.
- Pathology Prediction: By utilizing generative AI to analyze patterns in medical images, it is possible to predict or diagnose pathological disorders.
2. Drug Development and Discovery
Pharmaceutical research uses generative AI to improve drug development and discovery procedures. By examining molecular structures and biological data, including safety and efficacy profiles, artificial intelligence models can produce chemical compounds with desired features.
Compound generation: Generative AI models can expedite the process of drug discovery by efficiently analyzing a vast expanse of chemical space. By suggesting novel compounds with desirable features, these models optimize the search for possible drug candidates and speed up the process of identifying molecules that show promise for additional research and development.
Drug-drug interactions: The role of AI in digital transformation has predicted the possible drug interactions, helping researchers assess the efficacy and safety of mixing drugs. This skill is essential for the strategic planning of combination therapy, guaranteeing the best possible treatment results while reducing the hazards related to pharmaceutical interventions.
Atomwise is an additional instance that accelerates the process of identifying possible chemicals for different types of illnesses by forecasting possible drugs. In just six hours, artificial intelligence generated 40,000 new possible chemical molecules.
3. Personalized Medicine
To provide individualized treatment plans, generative AI synthesizes vast amounts of patient data, including genetic data, clinical notes, and electronic health records.
Generative AI algorithms can recognize patterns in a variety of datasets, forecast the course of diseases, and suggest the best course of action for therapy depending on the individual traits and medical background of each patient.
Generative AI analyses data from wearable devices to identify patterns and track health metrics like heart rate blood pressure etc. This allows for early intervention and individualized treatment regimens.
- Customized Treatment Regimens: Generative models can examine patient data, such as clinical data, medical history, and genetic information, to produce customized treatment plans. This can help in determining which treatments will work best for each patient as well as forecasting their unique reaction.
- Predictive Analytics for Treatment Response and Disease Progression: By combining several patient characteristics and analyzing massive datasets, generative AI may create predictive models that forecast treatment outcomes and disease progression. This optimizes patient care by assisting medical practitioners in making well-informed decisions about treatment plans.
- Clinical Decision Assistance in Real-time: Gen AI gives doctors evidence-based suggestions for individualized treatment plans based on a patient’s genetic profile in real-time.
- Support for ethical and legal compliance: Gen AI helps ensure that privacy laws and ethical standards are followed while handling ethical and legal issues around personalize medicine. This keeps patients compliant and fosters their trust.
- Genetic testing resource optimization is made possible by Gen AI, which improves genetic testing operations’ efficiency, streamlines workflows, and automates repetitive jobs. To overcome resource constraints and provide access to personalized medication, this is crucial.
4. Analysing Data and Conducting Medical Research
Data analysis and medical research provide a great deal of potential for generative AI techniques.
- Data Processing: Generative AI automates document reviews and data extraction while quickly analyzing large amounts of medical data. This simplifies administrative processes, freeing up researchers to focus more on critical aspects of their work.
- Medical Document Summarisation: Generative AI is very good at providing researchers with summaries of long medical records.
- Analyzing and Identifying Trends: This keeps researchers up to date on the most recent advancements, encouraging a proactive and knowledgeable strategy in the sector.
- Predictive Analytics Insights: Generative AI uses previous medical data to provide insights into possible outcomes.
5. Optimizing Clinical Trials
Health insurance procedures, especially those involving prior authorization and claims processing, which are frequently time-consuming and expensive for private payers, can be streamline with the use of generative AI technology. The current procedures for verifying prior authorization take around ten days on average.
With the use of this technology, advantages can be verified almost instantly by transforming unstructured data into structured formats. This entails precisely computing out-of-pocket expenses by taking into account patients’ particular benefits, the contracted rates of healthcare providers, and other pertinent variables.
6. Administrative Mandate
Effective administration of appointments: Gen AI streamlines scheduling by automating reservations and rescheduling, guaranteeing patient-friendly timeslots and improving overall scheduling effectiveness.
Streamlined billing and claims processing: AI automates these procedures, increasing financial workflows by decreasing errors, increasing accuracy, and speeding up the reimbursement cycle for healthcare providers.
Automation of data entry and extraction: Gen AI reduces the amount of human data entering and improves the accuracy of healthcare databases by automating tasks and extracting relevant information from a variety of sources.
Efficient communication management: AI-driven chatbots take care of standard questions, rescheduled appointments, and follow-ups, freeing up medical professionals to concentrate on more important tasks.
7. Bots and Virtual Assistants
Through dialogue, virtual health aides provide patients with easy access to medical services. AI chatbots that are integrated with popular EHR systems enable patients to book, reschedule, add themselves to waitlists, or cancel appointments without depending on human schedulers.
AI algorithms are used by virtual assistants to provide patients with individualize medication reminders and adherence alarms. This helps the AI in healthcare startups in providing timely reminders through mobile apps or smart devices. This in return helps the compliance in place and lowers the possibility of treatment disruptions.
How to Implement Generative AI in the Healthcare Industry?
The healthcare sector must adopt a rigorous strategy to ensure the successful installation and utilization of generative AI. This is a detailed how-to:
- Determine the Use Cases: Discuss the applications in healthcare that allow AI integration like drug discovery, medical image analysis, NLP for clinical documentation, personalized medicine, and predictive analysis.
- Gathering and Preparing Data: For GENAI model training, collect quality database. Make sure that the information is representative, diversified, and complies with legal and privacy requirements. To improve the accuracy of the model training, clean up and preprocess the data.
- Choose the Relevant Generative Model: Based on the identified use cases, select the appropriate one. Some of the examples of designs for the GENAI model are GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), VAEs (Variational Autoencoders), and GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer).
- Train the Model: The selected generative model is train using the prepared datasets. This can take a lot of computer power, depending on how complicated the work is. To get the best results for the particular healthcare application, fine-tune the model.
- Testing and Validation: Make use of different datasets that were not utilized for training to validate the generative model. Use the right settings, and test the dependencies, performance, and correctness to ensure the requirements are fulfilled.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Put in place systems to keep an eye on the effectiveness of the generative AI system. Update the model frequently with fresh data to increase accuracy and adjust to evolving healthcare environments.
- Transparency and Ethical Considerations: Make sure that the application of generative AI in healthcare is transparent and addresses ethical issues like prejudice in AI systems. Keep lines of communication open regarding how AI is affecting healthcare procedures with patients and stakeholders.
Conclusion
Healthcare with generative AI has a multigenerational potential to enhance patient outcomes and provide significant universal access. Although there are still some unresolved ethical concerns, healthcare professionals must begin utilizing new technologies to stay up-to-date and fully utilize their potential.
We should anticipate an even higher integration of AI technology into global healthcare systems as generative AI develops. This covers, among other things, developments in personalized medicine, virtual assistants, and medical image analysis.
A careful balance between the potential benefits and inherent hazards of generative AI is necessary for its effective incorporation into healthcare. Leaders need to evaluate every possible use in detail, weighing the benefits against any drawbacks.
Collaborate with CMARIX you are to develop resilient generative AI solutions customized for your industry-specific use case in healthcare and remain on the cutting edge of technological progress for enhanced healthcare provision.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Generative AI Help with Personalized Medicine?
Generative artificial intelligence models can anticipate the characteristics of possible therapeutic candidates, produce novel molecular structures, and enhance the safety and effectiveness of current compounds. The time and expense of medication development may be greatly shortened as a result.
Can Generative AI Improve Patient Communication?
Language difficulties that impede communication are a serious challenge in the healthcare industry. Real-time translation of medical information into many languages is possible using generative artificial intelligence (AI). This strengthens the bonds between patients and providers and increases patient knowledge while also fostering trust.
What Are the Future Trends in Generative AI for Healthcare?
Assistive technology will help patients with disabilities minimize the barriers they encounter in their daily lives, and generative AI models will aid improve health literacy by assisting in the breakdown of communication barriers between patients and clinicians.







