The development of location-based apps requires a team of developers to manage the different expertise needed. In the development process, programmers keep a keen perspective of the app’s future benefit and use. Geolocation apps have a lot of types of usage and provide a solution for a lot of problems and situations. Geolocation apps also provide innovation in areas such as marketing and ads. Let us take a quick look at the necessary steps to start-up the mobile app development of your location-based app.
1. Market Analysis
Interview or conduct a survey from potential users and find out what people need. Finding a way to fill a need is an excellent place to start when looking for opportunities for app development. As you study the market, you will see and observe what competitors are doing. From there, implement ways to make the service better.
2. Prototype Formulation
A logical structure begins to form in the conceptualization of the app. In setting up the initial formation of the app, developers get an idea as to what the end product is supposed to look and feel. Additional features are kept at a bare minimum to focus on the central app development.
Read More: Google Map Implementation in Angular with Dynamic Pins
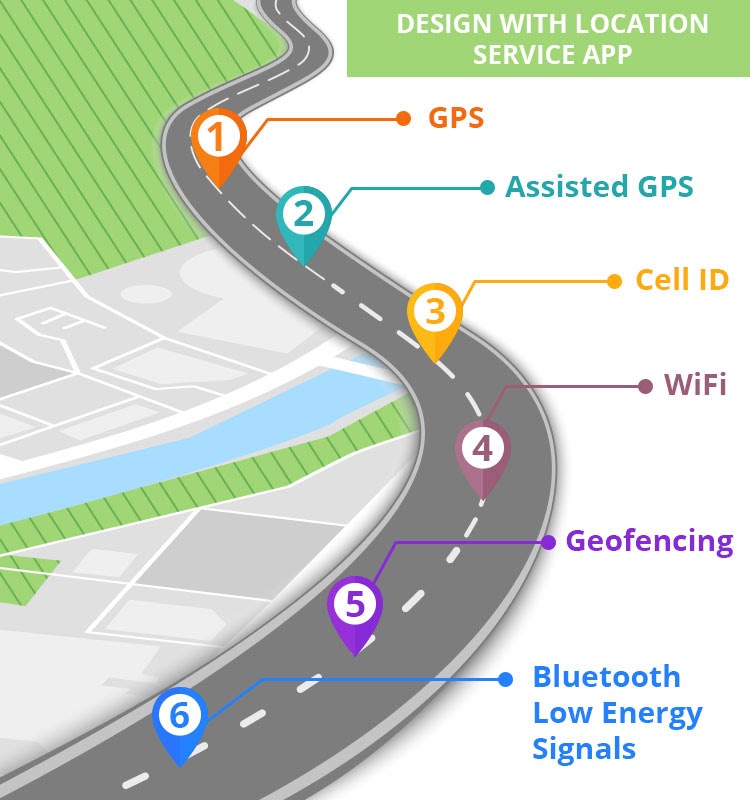
3. Design With Location Service App
As the app is location-based, developers must decide what type of location service app they would be incorporating with the app. There are numerous choices to select from, and the function and model of your app will determine what type of geolocation will provide solutions towards your goal.
GPS
A popular and useful feature within mobile devices and an outdoor type of geolocation app. Due to its popularity, people tend to look at GPS when talking about geolocation apps. Global Positioning System [GPS] allows users to access their current location with an accuracy that is within around 60 feet.
Assisted GPS
Another outdoor type of geolocation app and a kind of positioning system that provides a better quality of accuracy because it uses not just GPS, but it also utilizes the use of cell towers. The determination of location using these two factors significantly increases efficiency and accuracy.
Cell ID
As mentioned earlier, the use of the Cell ID dramatically increases the accuracy of Assisted GPS. But on its own, it is less accurate than GPS in providing location because it determines location through the help of cell towers. Especially once there is weak coverage such as outside of big cities. Cell ID is also classified as an outdoor type of geolocation app.
WIFI
This type of geolocation covers a small area but provides a much more precise and accurate location. WIFI can determine the location in two ways. One way is by deciding the strength of one’s signal with the assistance of WIFI points. Through the Received Signal Strength Indication [RSSI], the movement and location enable tracking in a small area through the strength or weakness of the signal. If the user is far away from the WIFI source, the signal indicator becomes weaker, and if the user is near, the signal indicator becomes stronger.
Geofencing
The concept used for geolocation by geofencing is somewhat similar to WIFI but using GPS as the source. This technology is built on GPS and determines how near or far a user may be located through established points. Geofencing uses three types of triggers to pinpoint the location of a particular device or individual.
Static triggers can track a mobile device or user when they enter or come into the vicinity of a point.
Dynamic triggers can track the location when the environment around the mobile device or user changes.
Combined triggers can track the location through the use of both static and dynamic triggers. These triggers are beneficial for marketing campaigns and ads. The determination of the precise location makes it possible to send the right marketing drive and advertisements to a mobile device.
Bluetooth Low Energy Signals
Both big companies, Apple and Google, made technologies that rely on Bluetooth low energy signals. The iBeacon and Eddystone can provide a high level of accuracy about a location. With the use of mobile devices’ proximity sensing capabilities, devices that are “always-on” benefit from this type of technology for geolocation.
4. Security
There are rules in developing apps that include provisions to protect a person’s privacy and secure and protect a person’s identifiable information such as geodata. A study made by emarketer showed that users are willing to share their personal and location information if they are assured of the top three things: increase of safety and security, if the information is necessary to enable service and if it saves them money.
Prioritizing the security features of your app is essential because building trust in today’s digital economy gains top priority in making your app’s name known in the industry. Also, penalties are being implemented when a breach of security occurs. Your app’s development will not go any further if one is not addressed. Giving users the choice to activate or deactivate their geolocation tracking feature also safeguards their security and privacy. They are the best person to know whether they need it or not. Some key security features of the app must address the access permissions granted to third party components. Make precautionary measures as you will use libraries and frameworks that are available and streamline them for your intended use.
Any vulnerability connected to third-party components must be dealt with accordingly. Geolocation apps provide transmission and reception of communication. Encryption is, therefore, a priority security feature. The privacy of users is at risk should this information be intercepted and deciphered. When you go for Android and iPhone app development services they have their particular security feature that you can use. Another security feature that you can implement with location-based apps is multiple-factor authentication. Some users are known to be picky and experience a bit of discomfort in having to enter another level of security for their app. But this level of protection is needed to cover any vulnerabilities in-app security. Multiple-factor authentication helps in minimizing attackers getting their hands on our data and communication details.
5. Suitable Coding
Your app will be integrated into the different platforms available out there. Each platform has a language that your app must be adapted to function it and take advantage of the various features of operating systems – having developers that have expertise with administering and providing programming suited to the different operating systems available in the digital market. The User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) will undergo development and further polishing to make the app more manageable for people to access and find what they need.
6. Quality Testing Your App
Quality control of a product is essential. Although the code’s written, tests prepared beforehand will address any foreseen bugs. Ongoing testing and further development keep the app’s quality high and up-to-date. As you and your team keep on testing the app, addressing vulnerabilities and bugs in the programming continues further.
7. Releasing For Consumer Use
With the initial stage finished, there are still a lot of things left to do – room for development to polish further what you would offer your users.
Further Development
The development goes even smoothly when experienced developers with specific expertise are part of the creation of the app. The process is ongoing and user support is integral in making the app better. With the actual usage of the app, some vulnerabilities and issues will arise as more people put real strain and demand upon the product. Addressing these concerns will further affect the viability of your app.